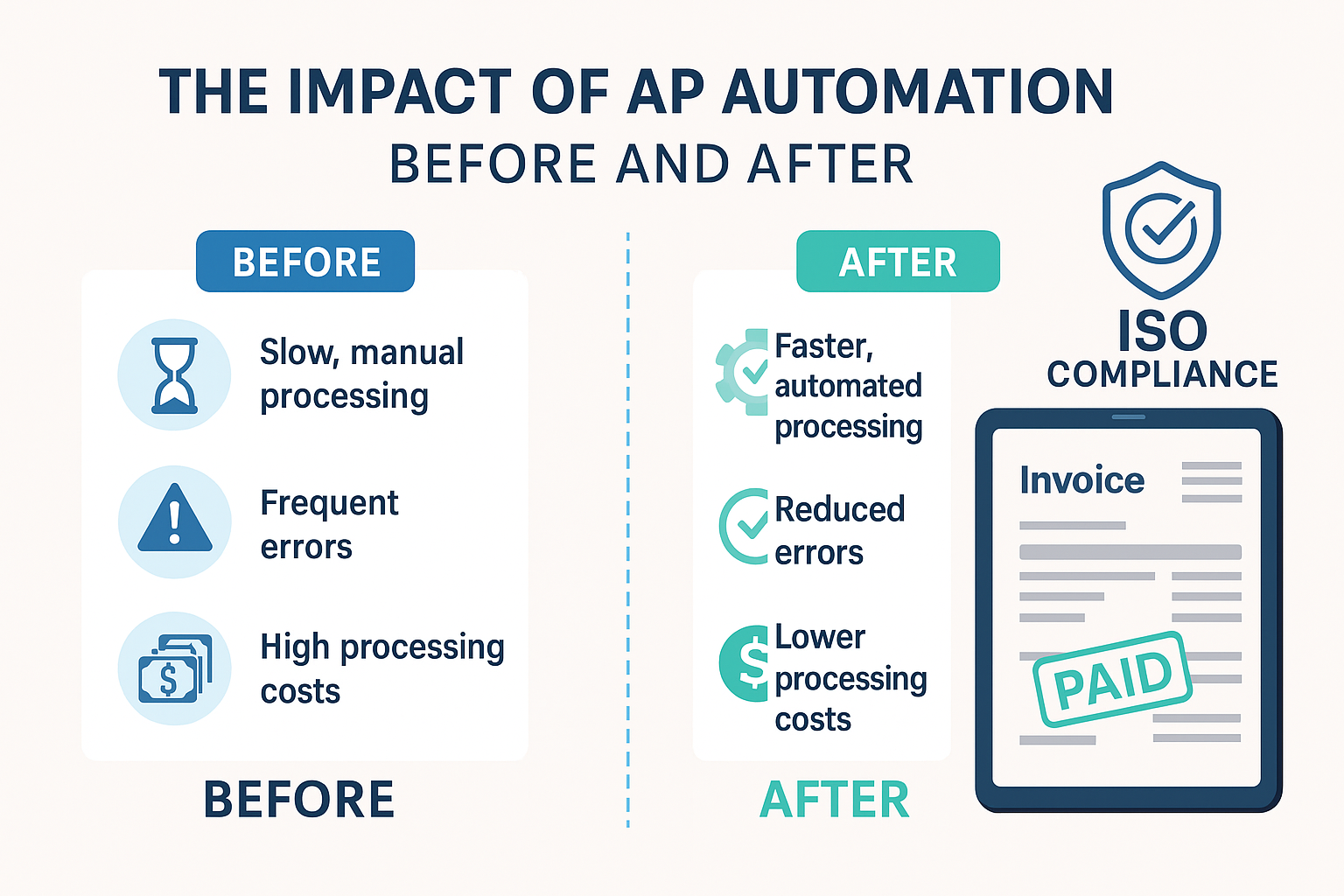
When organizations gear up for an ISO 9001 audit, the focus often gravitates toward production, quality control, and documentation processes. But there’s a lesser-known contributor that can tip the scales in your favor—Accounts Payable (AP). Surprisingly, modern AP automation tools not only enhance financial efficiency but also play a crucial role in strengthening ISO 9001 compliance.
Here’s how AP processes, especially when automated, can support your organization’s journey toward passing that all-important audit.
1. Documented Information Control (Clause 7.5)
ISO 9001 requires organizations to maintain documented information in a manner that ensures accuracy, retrievability, and protection against loss. Traditional AP processes involving paper invoices or scattered email approvals make this a challenge.
With AP automation:
Every invoice, approval, and payment record is stored in a centralized digital repository.
Version control and access logs are maintained automatically.
Auditors can trace transactions with a few clicks—ensuring compliance with documentation requirements.
2. Process Consistency and Control (Clause 8.5)
Quality standards thrive on repeatable, standardized processes. Manual AP workflows often involve inconsistencies in approvals, exceptions, and vendor communications.
Automation enables:
Rule-based workflows for approvals and thresholds.
Consistent validation of vendor details and payment terms.
Error reduction through real-time flagging of duplicates or mismatches.
The result? A transparent, controlled process that aligns with ISO’s emphasis on uniformity and predictability.
3. Risk-Based Thinking and Fraud Prevention (Clause 6.1)
ISO 9001 mandates that companies identify and mitigate risks that could impact quality. One such risk lies in unchecked financial transactions—leading to fraud, missed payments, or compliance violations.
An automated AP system offers:
Role-based access controls and audit trails.
Automatic checks for duplicate invoices or supplier anomalies.
Built-in compliance rules to flag exceptions before they escalate.
These features not only reduce financial exposure but also show auditors your proactive stance on risk management.
4. Supplier Relationship Management (Clause 8.4)
Strong vendor performance and reliable supply chains are essential to quality assurance. Delayed or inconsistent payments can harm supplier trust and service levels.
How AP automation helps:
Ensures timely payments through scheduled workflows.
Provides real-time communication on payment status.
Improves vendor satisfaction, which in turn boosts service quality—directly supporting ISO’s objectives.
5. Continuous Improvement (Clause 10.3)
ISO 9001 emphasizes the importance of using data to drive ongoing improvement. Manual AP systems often lack visibility into metrics such as invoice cycle time, error rates, or cost per invoice.
With automation, you gain:
Dashboards and analytics for identifying bottlenecks.
KPIs to benchmark AP performance over time.
Insights that feed into broader process improvement initiatives.
Your AP team becomes more than just a cost center—it becomes a partner in quality and compliance.
The Hidden Hero of Quality Compliance
While Accounts Payable may not be the first department considered in a quality management audit, its automation and alignment with ISO 9001 principles can be a significant advantage. From documentation control to supplier relationships and risk mitigation, an automated AP process helps you meet the expectations of auditors—and run a more efficient operation.
So next time you prepare for an ISO audit, don’t overlook your finance function. A smart, streamlined AP system could be the hidden asset that helps you ace it.