Blogs, News & Articles

How Pharma, Chemical, and Metal Industries Are Reinventing CoA Management with Automation
In highly regulated industries, Certificates of Analysis (CoAs) are not just routine paperwork — they are critical documents that ensure product quality, regulatory compliance, and customer trust. Industries like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and metals each rely heavily on CoAs but face unique challenges in managing them. As companies increasingly adopt CoA automation, it’s clear that while the end goal — accuracy, speed, and compliance — is common, the journey looks different across sectors.
In this post, we explore the specific hurdles faced by these industries and the best practices they are developing as they automate CoA management.
The Pharma Industry: Precision, Traceability, and Regulatory Pressure
Challenges:
Zero margin for error: Even a minor mistake in a pharmaceutical CoA — such as incorrect potency data — can have life-or-death consequences.
Complex validation needs: FDA regulations (like 21 CFR Part 11) require validated systems and meticulous audit trails.
High data volume and granularity: Each batch may require CoAs for multiple parameters like identity, purity, sterility, and stability.
Best Practices:
System validation first: Pharma companies invest heavily in validating automation tools to meet regulatory expectations.
End-to-end digital audit trails: Automation platforms are configured to track every edit, approval, and access to CoA data.
Integration with LIMS (Laboratory Information Management Systems): Seamless integration ensures lab results directly feed into CoA generation without manual re-entry.
The Chemicals Industry: Speed, Variability, and Global Compliance
Challenges:
Wide product variations: Different chemical formulations require flexible, customizable CoA templates.
Regulatory differences across borders: Compliance requirements vary greatly (e.g., REACH in Europe, TSCA in the U.S.), complicating document standardization.
Shorter lead times: Chemical buyers often demand fast turnaround, putting pressure on CoA generation.
Best Practices:
Template-driven automation: Systems use dynamic templates that auto-adjust based on product type, destination country, and customer-specific requirements.
Multilingual support: Automated CoAs are configured to generate in different languages based on shipment locations.
Automated compliance checks: Built-in rule engines verify CoA content against country-specific regulations before dispatch.
The Metals Industry: Volume, Format Diversity, and Certification Authenticity
Challenges:
Massive documentation needs: Every coil, sheet, or bar of metal typically requires a dedicated CoA, creating overwhelming volumes.
Format inconsistencies: Suppliers, mills, and customers often use different CoA layouts and terminology.
Fraud risks: In high-value transactions, falsified CoAs can have major financial and reputational repercussions.
Best Practices:
Advanced OCR and AI extraction: Automation tools read and standardize CoAs from different suppliers into a common format.
Blockchain integration for authenticity: Some metals companies are experimenting with blockchain-backed CoAs to prevent tampering.
Customer self-service portals: Allowing customers to access CoAs directly via secure online platforms reduces administrative load and enhances transparency.
Key Lessons Across Industries
While each sector faces unique pressures, a few universal lessons stand out:
Prioritize data integrity: Automation must not compromise on data accuracy, validation, and traceability — especially in regulated environments.
Design for flexibility: Systems must handle product variations, customer-specific demands, and evolving compliance norms.
Drive integration: Linking CoA automation with broader systems like ERPs, LIMS, and CRM platforms ensures consistency and eliminates manual steps.
Plan for audits: Automation tools should make it easier, not harder, to respond to internal and external audits with complete, tamper-proof CoA records.
Automating CoA generation and management is becoming a competitive and compliance necessity across regulated industries. However, a one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t work. By learning from the experiences of sectors like pharma, chemicals, and metals, companies can implement smarter, more resilient CoA automation strategies that meet their industry's specific demands while future-proofing their operations.
As the landscape continues to evolve, one thing is clear: those who invest early in CoA automation will be better equipped to deliver quality, speed, and trust in an increasingly demanding market.

Achieving ISO 9001 Goals Faster with COA-Integrated QMS Software
For manufacturers striving to maintain quality excellence and meet global standards, ISO 9001:2015 remains the benchmark for building trust and consistency in product delivery. At the heart of this compliance journey lies the need for reliable documentation, accurate testing records, and controlled processes. This is where COA (Certificate of Analysis) automation becomes a game-changer—especially when integrated into Quality Management System (QMS) software.
Why COA Matters in ISO Compliance
A Certificate of Analysis is a critical document that certifies a product’s compliance with predefined specifications, such as chemical composition, mechanical properties, or microbiological content. In industries like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, metals, and food processing, COAs are not just quality markers—they are regulatory necessities.
Yet, many organizations still rely on manual data entry and fragmented systems to manage these certificates, leading to inconsistencies, delays, and compliance risks.
COA Automation: A Perfect Fit for ISO 9001
Let’s explore how COA automation directly supports the key clauses of ISO 9001:2015, transforming your QMS software into a proactive compliance engine.
1. Evidence-Based Decision Making (Clause 9.1)
ISO 9001 calls for data-driven quality decisions. COA automation ensures that test results are accurately captured from labs or supplier systems using OCR and AI tools. The result? Reliable data sets that allow quality teams to take informed decisions with full traceability.
2. Control of Documented Information (Clause 7.5)
Maintaining version-controlled, accessible, and secure documentation is a requirement. Automated COAs are digitally stored within the QMS, indexed by batch or supplier, and available at a click—removing the chaos of paper trails and misplaced files.
3. Operational Control (Clause 8.5)
Quality assurance depends on releasing only compliant batches. Automated COAs link directly to product specifications and flag out-of-spec results in real time, preventing faulty shipments and ensuring product integrity.
4. Customer Focus (Clause 5.1.2)
When customers demand timely and accurate documentation, COA automation delivers. It enables fast generation of tailored COAs per customer specs, enhancing transparency and building trust.
5. Risk-Based Thinking (Clause 6.1)
Manual COA workflows introduce errors and slow response times. Automation mitigates these risks by enforcing data validation rules, reducing human error, and offering early warnings for non-conformities.
6. Continual Improvement (Clause 10.3)
Automated COAs feed valuable quality trends into your QMS. With the right analytics, businesses can detect recurring issues, improve supplier performance, and optimize manufacturing processes—all aligning with ISO's focus on continuous improvement.
A Real-World Example
Consider a pharmaceutical manufacturer managing hundreds of raw material lots weekly. With COA automation integrated into their QMS, each incoming batch is automatically verified against specifications. Deviations trigger non-conformance workflows, while compliant batches generate instant COA documents for customer and regulatory records. The result? Faster release cycles, zero data-entry errors, and audit readiness 24/7.
Achieving ISO 9001 compliance is not just about ticking checkboxes. It’s about building systems that ensure product quality, minimize risk, and enhance customer satisfaction. COA automation plays a vital role in this ecosystem by transforming a traditionally manual, error-prone process into a streamlined, intelligent workflow—right within your QMS software.
If you're aiming for tighter control, better traceability, and true ISO alignment, it’s time to explore COA automation as a strategic lever in your quality transformation journey.

Traceable Materials, Smarter ESG
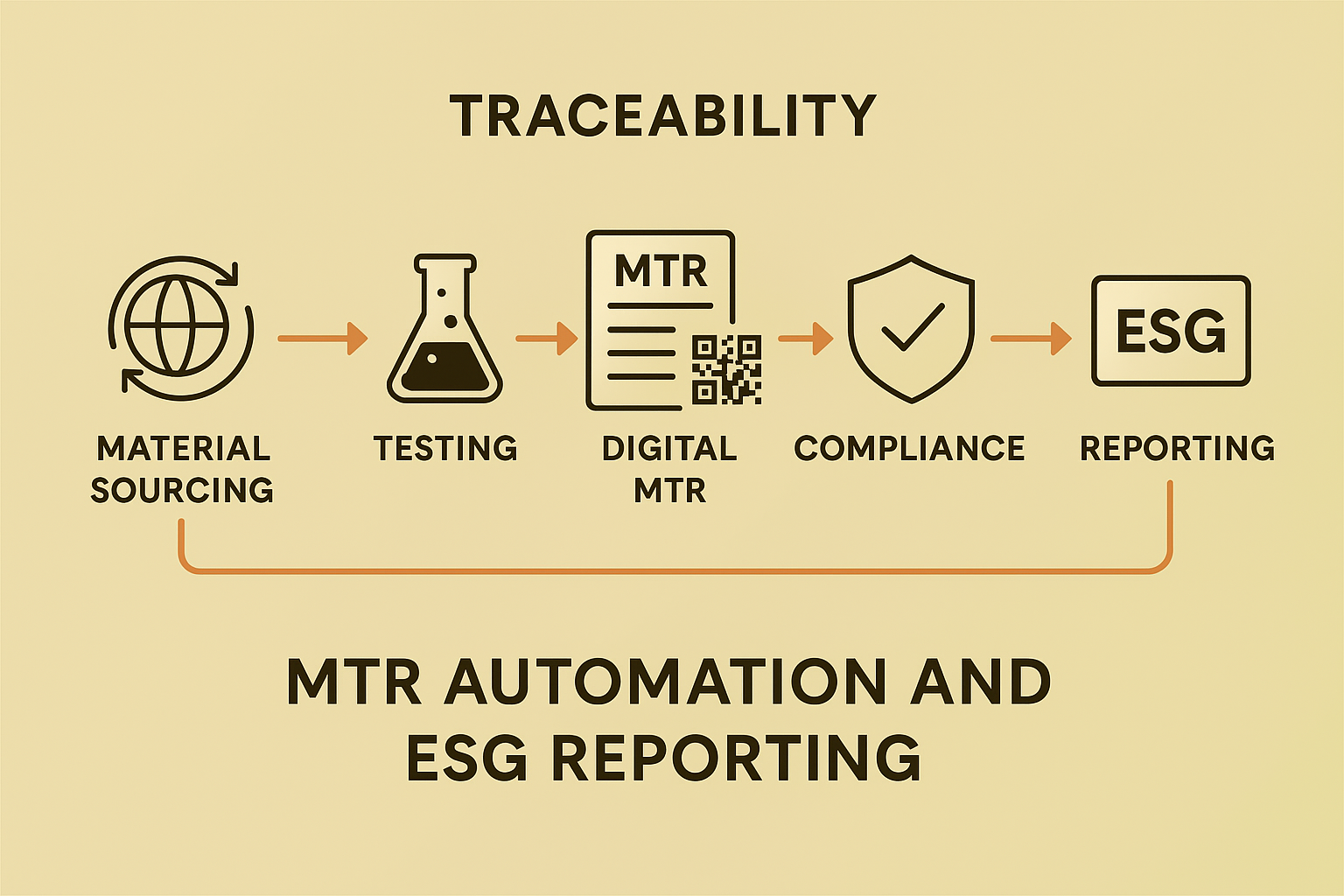
Sustainability reporting is only as strong as the data behind it. As industries embrace Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals and circular economy principles, the demand for transparency and traceability across the supply chain has never been higher. At the intersection of compliance, innovation, and sustainability lies a game-changer: automated Material Test Reports (MTRs).
What Are MTRs and Why Automate Them?
Material Test Reports document the chemical, mechanical, and physical properties of metals and other materials used in manufacturing. Traditionally handled manually, MTRs are essential for quality assurance and regulatory compliance—but they’re also ripe for transformation.
Automating MTRs with AI-driven document extraction, Optical Character Recognition (OCR), and system integration eliminates human error, accelerates reporting, and provides clean, structured data in real time. But beyond efficiency, this automation fuels deeper goals—especially around ESG reporting.
ESG Reporting Needs Reliable Data
Sustainability efforts are no longer optional. Companies are now required to disclose detailed environmental impacts, material sourcing, and production processes to regulators, investors, and stakeholders. Manually managing this data is time-consuming and prone to inconsistencies. Enter automated MTRs, which offer:
Accurate traceability of raw materials and suppliers
Instant access to compliance documentation
Streamlined audits for environmental certifications
Real-time updates for lifecycle tracking
With every material batch linked to a digital, tamper-proof trail, organizations can confidently back up their ESG claims.
Supporting the Circular Economy
The circular economy promotes using resources for as long as possible, extracting maximum value before recovery and regeneration. To make this work, manufacturers must know where materials come from, how they perform, and whether they can be reused or recycled safely.
Automated MTRs help close this loop by:
Tracking material lineage and quality from origin to end-use
Highlighting recyclable components or grades
Enabling predictive maintenance through material performance data
Reducing waste and overproduction through better inventory visibility
This isn’t just smart manufacturing—it’s responsible manufacturing.
Real-World Example: Metals and Mining
In the metals industry, ESG regulations are tightening, especially regarding carbon emissions and ethical sourcing. Companies using MTR automation are now able to:
Prove the origin of conflict-free materials
Validate the mechanical integrity of recycled steel
Benchmark emissions against global standards
These capabilities are helping companies not only reduce risk but enhance their sustainability ratings—a key factor in investor and customer decisions.
The Future: Integrating MTR Data into ESG Dashboards
Forward-thinking companies are already linking automated MTR data into ESG analytics dashboards, giving them:
Instant KPI tracking for sustainability goals
Alerts on material non-compliance
Visualizations for boardroom and stakeholder presentations
This integration brings ESG and quality assurance under one digital roof—driving smarter decisions and stronger compliance.
As ESG and circular economy pressures rise, automating MTRs goes from being a nice-to-have to a strategic necessity. By ensuring material traceability, quality, and transparency, MTR automation isn't just about compliance—it's about building a future where performance and responsibility go hand in hand.
Traceable materials lead to traceable impact. That’s the future of sustainable manufacturing.

Fighting Fakes: How Smart AP Automation Detects AI-Generated Image Fraud in Invoices
Last year, a mid-sized U.S.-based manufacturing firm narrowly avoided a six-figure fraud. A vendor had submitted an invoice with seemingly legitimate documents—logoed letterhead, itemized charges, and even a stamped delivery note. It wasn’t until their AI-powered accounts payable (AP) automation flagged inconsistencies in the image metadata that the finance team discovered the stamp and signature were AI-generated overlays. The company had almost paid a scammer.
As generative AI becomes more sophisticated, fake images are starting to pass off as real, posing a new risk for corporate finance functions. And for AP teams dealing with dozens or hundreds of vendor invoices daily, this is no longer science fiction—it’s a growing operational threat.
The Rise of AI-Generated Image Fraud
AI tools like Midjourney, DALL·E, and Stable Diffusion are no longer just for artists and marketers. Fraudsters have begun using these platforms to forge documents with chilling accuracy. A vendor logo can be recreated in seconds, and fake delivery proofs or digitally signed receipts can be layered seamlessly over real backgrounds.In some recent phishing cases, fake invoices were supported with doctored screenshots of bank transfers, or photoshopped GRNs (Goods Receipt Notes) from real suppliers—making it extremely difficult for the human eye to detect inconsistencies.
Why AP Teams Need to Worry
Traditionally, invoice verification has involved a mix of human checks and basic OCR tools. But when images appear authentic at first glance, and supporting documents are carefully tailored to match past transactions, a busy AP team may not catch the deception—especially under tight processing SLAs.Beyond financial losses, approving a fraudulent invoice can damage vendor relationships, delay legitimate payments, and create compliance issues during audits.
How Smart AP Automation Can Help
Enter AI-powered AP automation systems—now equipped with intelligent image verification tools. These platforms don’t just read data; they analyze it.Here’s how they fight AI-generated image fraud:
Logo and Signature Pattern Matching: Machine learning models trained on legitimate vendor documents can flag mismatches in logo shape, pixel density, or signature alignment—even if they look “right” to the human eye.
Cross-Referencing Historical Documents: Smart systems compare current documents against past verified submissions from the same vendor, flagging anomalies in stamp placement, color variations, or inconsistent formatting.
Metadata and Timestamp Validation: Image forensics can detect if an image has been altered, duplicated, or created using a generative model. For example, if an invoice claims to be from July but the image metadata says it was created in September, the system raises a red flag.
Source Verification: Some platforms now check if the logos or documents have been lifted from public sources (e.g., reverse-image searches) and warn against possible impersonation.
A Realistic Scenario
Let’s say a logistics vendor submits a $22,000 invoice with an attached delivery note showing a signature from the warehouse manager. Smart AP automation checks the document’s visual signature against its historical database and finds no match in the signature pattern. Simultaneously, the system notices the image was created using a known AI-generation tool, based on metadata fingerprints.The invoice is paused, and the finance head is alerted. A quick call to the warehouse confirms that no such delivery took place. Fraud is averted.
The Human-AI Alliance
While smart AP automation can handle the first line of defense, fraud detection still benefits from human judgment. AI can flag suspicious documents, but the final verification often needs context—such as recent vendor behavior, ongoing disputes, or emergency procurement orders.That’s why the future of fraud prevention in AP lies in a hybrid model: smart systems that do the heavy lifting, and informed finance professionals who make the final call.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Fake images are no longer limited to social media hoaxes—they’ve entered the world of business transactions. But while generative AI is giving fraudsters powerful tools, it’s also arming finance teams with sharper defenses.
Smart AP automation is not just a matter of efficiency anymore—it’s become a critical safeguard. Because in an age where fakes look real, the ability to detect the invisible could be the difference between profit and peril.

Accelerating Digital Manufacturing ROI with Automated MTR Insights
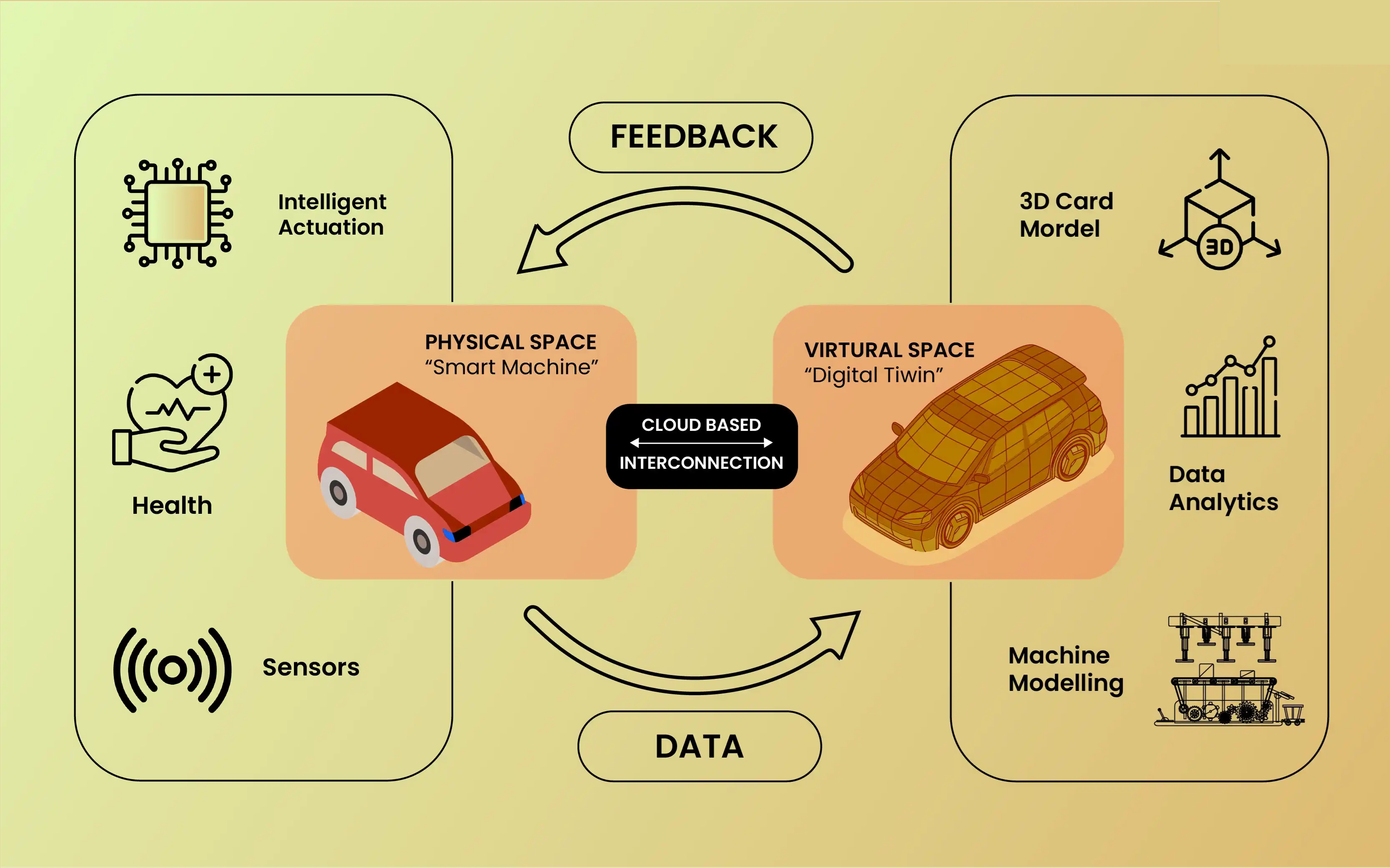
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical products, processes, or systems. Fed by real-time data from sensors, machines, and enterprise systems, these dynamic models help manufacturers simulate performance, monitor production, and predict maintenance needs—all without touching the shop floor.
But for digital twins to be truly effective, they must mirror not just the design of a product, but also the exact materials used to build it. That’s where Material Test Reports (MTRs) come in. These documents contain vital information about the mechanical and chemical properties of metals and alloys used in production.
In most organizations, however, MTRs are still processed manually—stored as PDFs, emailed, or entered into systems by hand. This introduces errors, delays, and data blind spots that compromise the integrity of digital twin models.
The fix? Automated MTR integration, which ensures material traceability and quality validation at every step of production—unlocking the full potential of digital twins.
Why Accurate Material Data Matters to Digital Twins
Digital twins rely on precise, real-world data to simulate and analyze how a product will behave under various conditions. If the materials listed in the design don't match what's used on the shop floor, predictions become unreliable and product performance is at risk.
Enter MTRs—documents that verify material specs like tensile strength, hardness, chemical composition, and heat numbers. By automating the extraction and integration of this data, manufacturers ensure their digital twins reflect real, production-level conditions.
How Automated MTR Integration Enhances Digital Twin Accuracy
Fast, Accurate Data Capture via OCR + AI
Intelligent systems extract relevant data—such as material grade, lot numbers, and mechanical properties—from MTR PDFs using Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and AI/ML.Seamless Linking to ERP, PLM, and MES Systems
Once digitized, MTR data is automatically linked to material batches, production orders, and CAD models, ensuring a seamless data trail from raw input to finished product.Better Simulation and Quality Control
With real-world material properties fed directly into simulation tools, engineers can test product performance with greater accuracy—reducing prototypes and failures.Proactive Risk Detection
Automated systems can flag non-compliance between design specs and received materials, enabling real-time alerts and faster decision-making.
Case Study: Smart Aerospace Manufacturing
An aerospace component manufacturer integrated MTR automation into their digital twin ecosystem. The system automatically extracted and validated MTRs upon receiving materials, linking each batch to its corresponding digital model.
Impact:
80% reduction in manual QA effort
Full material traceability from supplier to part
Regulatory audits completed in hours, not days
Material Traceability Is No Longer Optional
As global supply chains grow more complex and compliance standards tighten, manufacturers must be able to prove what went into every product—and where it came from.
Automated MTR integration delivers:
End-to-end material traceability
Confidence in simulation and quality outcomes
Better collaboration between procurement, production, and engineering teams
A Smarter Twin Starts with Smarter Materials Data
The promise of digital twins lies in their accuracy and adaptability. To build and maintain that integrity, manufacturers must automate the flow of real-world material data—starting with MTRs.
In smart manufacturing, digital twins aren’t just models. They’re decision-making engines. And when fueled by accurate, automated MTR data, they help companies design better, build faster, and operate with confidence.