Blogs, News & Articles

Digitizing the Supply Chain: Automating Certificates of Analysis
In industries where quality and compliance are non-negotiable—such as pharmaceuticals, metals, and food—trust across the supply chain is paramount. One of the most critical tools in building and maintaining this trust is the Certificate of Analysis (CoA). Traditionally, these documents were manually generated and exchanged, often leading to delays, inconsistencies, and errors. But today, automation is transforming the CoA landscape, injecting speed, accuracy, and transparency into supplier-customer relationships.
What Is a Certificate of Analysis (CoA)?
A Certificate of Analysis is an authenticated document that certifies a product’s compliance with required specifications and regulatory standards. It details the composition, quality, and safety parameters of a product batch—vital information for downstream stakeholders. In pharmaceuticals, a CoA may confirm the purity and potency of an active ingredient. In the metals industry, it might verify tensile strength and composition. In food, it ensures nutritional content and absence of contaminants.
The Problem with Manual CoAs
Despite their importance, CoAs have traditionally been managed through manual processes—scanned PDFs, emails, or handwritten documents. This results in several challenges:
Inconsistency in formats across suppliers makes interpretation difficult.
Human errors during data entry can jeopardize quality assurance.
Delayed documentation affects just-in-time supply chains.
Fraud risks arise from forged or altered CoAs.
In such high-stakes industries, these risks are not just operational hurdles—they can lead to regulatory non-compliance, product recalls, and loss of customer confidence.
How CoA Automation Solves the Problem
Automated CoA systems leverage intelligent document processing (IDP), machine learning, and integrated data pipelines to generate, validate, and transmit CoAs in real time. Here's how this improves trust and transparency:
1. Real-Time Traceability
Automated systems can generate CoAs directly from quality control instruments or ERP databases, ensuring that every value reported is sourced from validated data. This traceability builds confidence among customers and regulators alike.
2. Standardized Formats
Using structured data templates and APIs, companies can issue CoAs in consistent digital formats across all suppliers and plants, making it easier for downstream customers to read and verify them.
3. Error-Free Documentation
By minimizing manual intervention, automation significantly reduces the scope for typographical and reporting errors—ensuring that what’s delivered is what was tested and approved.
4. Faster Turnaround Times
Automated CoAs can be generated and shared instantly upon batch clearance. This accelerates shipment readiness and enhances on-time delivery metrics.
5. Digital Signatures and Authentication
Security features like blockchain stamping or digital signatures ensure that the CoA is tamper-proof, bolstering trust in its authenticity.
Industry Impact: Pharma, Metals, and Food
Pharmaceuticals
With tight FDA and EMA regulations, automated CoAs ensure batch release documentation is audit-ready and available in real-time, reducing the time to market for life-saving drugs.
Metals
For steel, aluminum, and alloy manufacturers, CoAs validate material strength, composition, and tolerance. Automation improves coordination between mills and OEMs, especially in sectors like automotive and aerospace where specs are mission-critical.
Food and Beverage
From allergen declarations to microbial tests, food companies rely on CoAs for consumer safety. Automation ensures rapid response to contamination risks and transparent labeling for health-conscious consumers.
Building Trust Across the Chain
In an era of globalized supply chains and increasing demand for ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) transparency, automated CoAs offer more than compliance—they provide a competitive advantage. By delivering timely, accurate, and verifiable information to customers, companies can foster deeper partnerships, reduce disputes, and build brand credibility.
----------
From the factory floor to the customer’s hands, trust must be continuously earned—and data is at the core of that trust. Automating Certificates of Analysis is not just a technological upgrade; it is a strategic imperative for businesses that aim to be transparent, agile, and accountable. As more industries adopt this approach, the supply chain itself becomes smarter, safer, and more synchronized.

Selecting the Right IDP Vendor: What CIOs and CTOs Should Know
As businesses increasingly look to intelligent document processing (IDP) to automate data extraction and improve accuracy, the choice of the right vendor becomes a critical decision for CIOs and CTOs. With a growing number of solutions in the market, it’s easy to get dazzled by flashy AI claims. But selecting an IDP vendor should go beyond demos and buzzwords. Here’s what technology leaders should consider to ensure a successful deployment that aligns with business objectives.
1. Technology Fit and Integration Capability
An IDP solution is not a standalone tool—it must seamlessly integrate with your existing technology stack, whether it’s ERP, CRM, BPM, or RPA systems. CIOs and CTOs should evaluate:
API readiness: Does the IDP platform offer well-documented APIs for easy integration?
Connector ecosystem: Are pre-built connectors available for your core platforms (e.g., SAP, Salesforce, ServiceNow)?
Cloud/on-prem flexibility: Can the solution be deployed in your preferred environment?
2. Accuracy and Scalability
It’s essential to look beyond vendor-reported accuracy rates in pilot scenarios. Consider:
Real-world performance: Ask for case studies or references from industries similar to yours.
Scalability proof points: Can the solution handle increasing document volumes without degradation in speed or accuracy?
3. AI and ML Capabilities
Modern IDP relies on AI/ML to handle unstructured and semi-structured data. CIOs/CTOs should evaluate:
Adaptability: Can the model learn from corrections and improve over time?
Pre-trained models: Does the vendor offer domain-specific models for faster deployment (e.g., invoices, purchase orders, medical records)?
Human-in-the-loop: Is there an interface for exception handling and model retraining?
4. Security and Compliance
Since IDP often processes sensitive data, security cannot be an afterthought. Key aspects include:
Data residency and sovereignty options
Compliance with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2
Robust encryption at rest and in transit
5. Vendor Stability and Roadmap
Investing in IDP is a long-term decision. It’s critical to assess:
Financial health and market reputation of the vendor
Support model and SLAs
Product roadmap alignment with your digital transformation vision
6. Cost Structure and ROI
Transparent pricing and clear ROI potential are essential. Evaluate:
Licensing models (per page, per document, subscription)
Hidden costs (customizations, support, scaling fees)
Potential savings in manual effort, error reduction, and turnaround times
Choosing the right IDP vendor is as much about strategic alignment as it is about technology features. CIOs and CTOs should engage stakeholders across operations, compliance, and IT to create a robust evaluation framework. A well-chosen IDP solution can significantly advance your automation journey—turning document chaos into structured, actionable data.

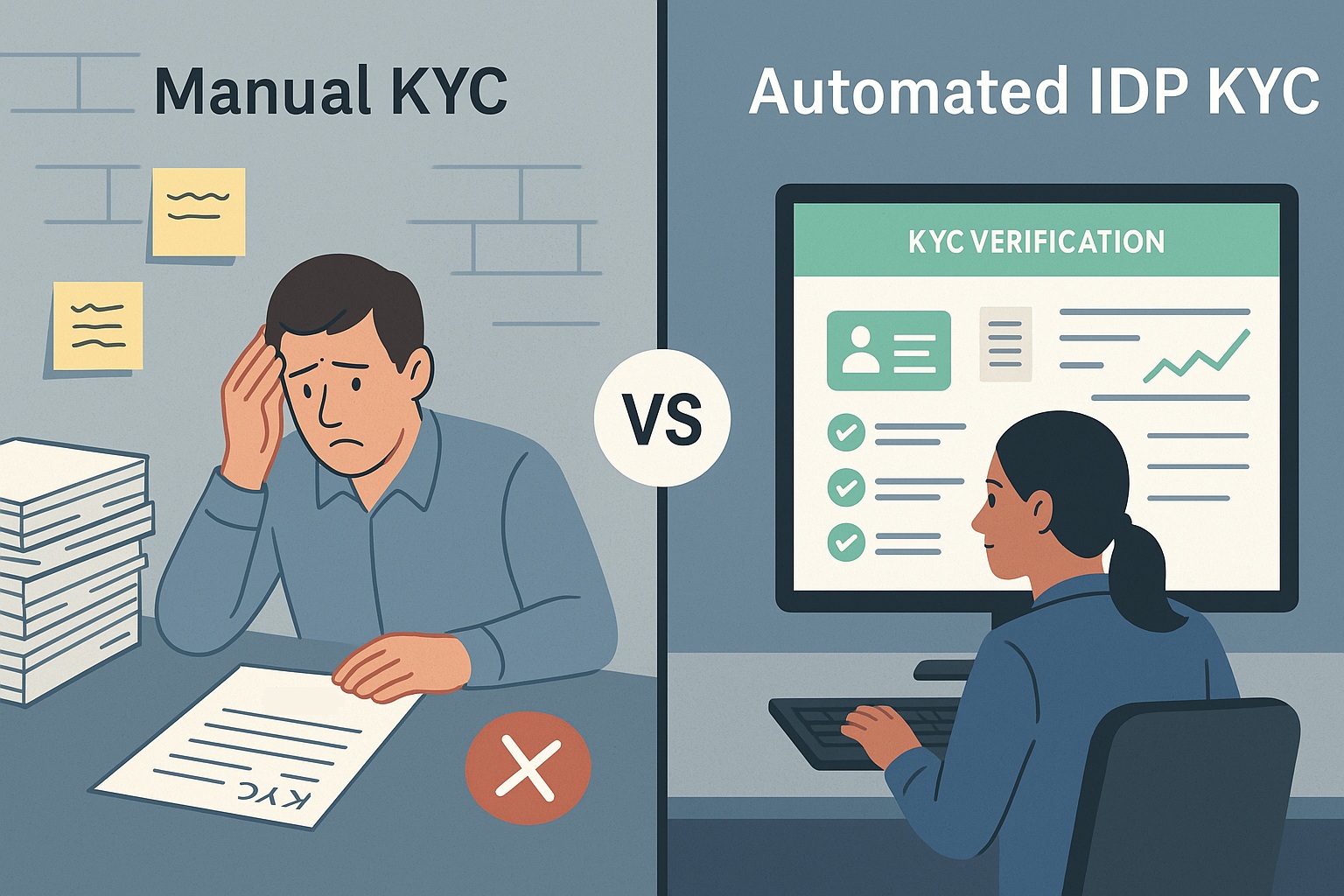
The Role of IDP in Audit-Ready KYC Processes
As regulatory oversight intensifies in the U.S. financial services sector, businesses must ensure that their KYC (Know Your Customer) documentation is not only complete and accurate but instantly audit-ready. With compliance mandates from agencies like FinCEN, the OCC, and state-level regulators, maintaining organized, verifiable, and accessible records has become a strategic priority. Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) is emerging as a key enabler of this transformation.
Why Audit-Readiness Matters in KYC
Whether you’re a traditional bank, a credit union, or a fintech disruptor, your KYC practices are under constant scrutiny. Auditors—internal or regulatory—look for properly validated documents, traceable workflows, and compliance with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) standards. But legacy systems and manual workflows are often ill-equipped to handle this demand, leading to bottlenecks, data discrepancies, and audit risk.
This is where IDP steps in.
How IDP Powers Audit-Ready KYC
✔️ Precision Extraction with Traceable Logs
IDP uses AI/ML to extract key data fields—names, addresses, ID numbers—from documents like passports, driver’s licenses, and utility bills. Each step is logged, providing a transparent digital trail that auditors can easily verify.✔️ Real-Time Document Validation
By cross-referencing inputs against government databases or internal systems, IDP ensures documents are authentic and current—cutting down manual review time while increasing audit confidence.✔️ Smart Categorization and Checklist Mapping
IDP automatically classifies documents (e.g., W-9, Articles of Incorporation) and maps them to KYC requirements, ensuring consistency across all customer files and eliminating gaps.✔️ Scalable Across High Volumes
From startups processing a few hundred clients to large enterprises with millions of accounts, IDP scales effortlessly—keeping audit compliance uniform at every level.✔️ Built-in Regulatory Alignment
Top IDP platforms are designed with U.S. regulations in mind—supporting compliance with the Patriot Act, GLBA, SOX, and state-specific mandates through role-based access controls and secure storage.Real-World Example: Fintech Onboarding
Consider a U.S.-based fintech that provides instant credit lines to SMBs. The firm had to manually review hundreds of EIN letters, business registration docs, and tax forms—often facing delays and errors. By adopting IDP, they automated 80% of document verification, organized files for audit readiness, and reduced their audit prep time by 60%.
Audit-readiness is no longer about reactive documentation—it's about proactive intelligence. IDP empowers financial institutions and fintechs to create KYC systems that are compliant by design, scalable by default, and efficient by necessity. For organizations aiming to meet regulatory scrutiny without sacrificing agility, IDP offers a clear path forward.

How AP Automation Helps Healthcare Companies Ensure Regulatory Compliance
In the healthcare sector, accuracy, speed, and compliance are not just operational goals—they are regulatory imperatives. From managing vendor payments to maintaining proper audit trails, Accounts Payable (AP) is a critical function that directly impacts a provider's financial health and legal standing.
As the healthcare industry becomes increasingly complex and regulated, manual AP processes are proving unsustainable. That's why a growing number of hospitals, clinics, and pharmaceutical companies are embracing AP automation—not only to improve efficiency but also to ensure regulatory compliance at every step.
The Compliance Challenge in Healthcare AP
Healthcare organizations must adhere to a range of financial regulations and standards such as:
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) for data privacy
SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act) for financial reporting integrity
CMS and Medicaid billing rules
IRS requirements for 1099 vendor reporting
Internal audit standards for fraud prevention
Manually processing invoices and payment approvals can lead to data entry errors, missed deadlines, duplicate payments, or worse—non-compliance that triggers audits or penalties.
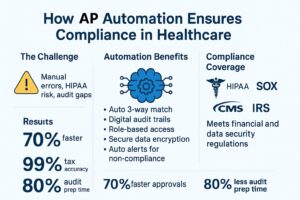
How AP Automation Solves the Compliance Puzzle
1. Audit-Ready Digital Trails
AP automation platforms create timestamped, immutable records of every action—from invoice receipt to approval to payment. This ensures full audit traceability, a key requirement for SOX and HIPAA compliance.
2. Automated 3-Way Matching
By automatically matching invoices with purchase orders and goods received notes, automation reduces the risk of overpayment or fraudulent billing—strengthening internal controls and ensuring accurate reporting.
3. Data Encryption & Access Control
Modern AP solutions are built with enterprise-grade security, including role-based access and encryption, which aligns with HIPAA’s data protection mandates.
4. Regulatory Document Retention
Most healthcare regulations require financial records to be retained for several years. Automated systems digitally store and organize documents, making them easy to retrieve during inspections or audits.
5. Real-Time Compliance Alerts
Some platforms offer built-in alerts and AI-driven analytics to flag suspicious transactions, missing tax information, or expired vendor credentials—allowing compliance teams to act quickly.

Real-World Example: Hospital Network Case Study
A multi-location U.S. hospital group with over 800 vendors and 50,000 annual invoices faced recurring issues in invoice reconciliation and 1099 tracking. After implementing an AI-based AP automation solution:
Invoice approval time dropped by 70%
1099 error rates fell below 1%
Internal audit preparation time was reduced from weeks to days
The organization not only streamlined AP but also achieved a higher compliance rating in its next financial audit.
Bonus: Integration with ERP and EHR Systems
Many healthcare organizations operate on platforms like SAP, Oracle, or Epic. Modern AP automation tools offer seamless integration with these systems—ensuring that financial compliance is maintained across departments without duplication or data silos.
In a sector where regulatory scrutiny is high and error margins are thin, automating accounts payable is no longer optional—it’s essential. Healthcare companies that invest in AP automation not only gain efficiency and cost control but also build a robust compliance framework that can withstand audits, scale with growth, and ultimately, improve patient care by freeing up financial resources.

How ML Handles Variability in Certificate of Analysis Formats
Certificate of Analysis verifies that products meet specified standards before reaching the customer or the market. However, a persistent challenge across organizations is the lack of standardization in CoA formats. These documents vary widely by supplier, product, geography, and even over time—posing major hurdles for automation and compliance.
This is where Machine Learning (ML) comes into play. Unlike rule-based systems that break under inconsistency, ML adapts and evolves—making it ideal for managing CoA variability at scale.
The Challenge: CoA Format Chaos
A single enterprise might receive CoAs from hundreds of suppliers, each using different formats, languages, data placements, and terminologies. One supplier may list "Moisture %," another might call it "Water Content," while a third might abbreviate it as "H2O." Manual processing is slow, error-prone, and unsustainable—especially when compliance and customer satisfaction are on the line.
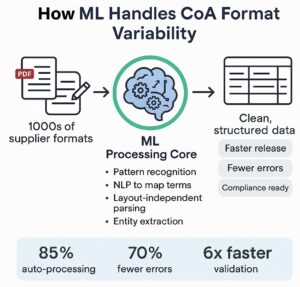
How ML Tackles the Problem
1. Smart Pattern Recognition
ML models can be trained on large volumes of CoA documents to recognize patterns, even when layouts differ. Whether the data is embedded in a table, embedded in paragraphs, or scattered across scanned PDFs, ML can identify and map it to structured fields.
2. Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
Using advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP), ML models understand different ways the same parameter can be represented. They learn from context—so "Total Impurities" and "Combined Impurities" can be treated as the same parameter based on historical training data.
3. Layout Agnosticism
Traditional data extraction relies on fixed templates. ML-driven IDP (Intelligent Document Processing) engines go beyond that by learning from layout variation. They adapt to new document structures, eliminating the need for reconfiguring templates every time a supplier updates their format.
4. Entity Extraction and Label Mapping
ML models can tag and extract relevant entities—like compound names, units, and test values—then match them against a predefined master list. This creates standardized data from highly variable inputs.
5. Continuous Learning
The beauty of ML is that it gets smarter over time. Every manual correction made by a human reviewer can be used to retrain the model, improving its accuracy and adaptability in handling future CoAs.
Real-World Example
A global pharmaceutical company receives CoAs from over 1,000 vendors worldwide. Previously, a team of 25 quality assurance personnel spent hours validating each document manually.
After deploying an ML-based CoA automation solution:
Over 85% of documents were processed automatically.
The error rate dropped by 70%.
Validation cycle time reduced from 48 hours to under 6.
All this while seamlessly handling new document formats without any manual reprogramming.
The Payoff: Speed, Accuracy, and Compliance
By embracing ML to manage CoA variability, companies benefit from:
Faster product release cycles
Improved data accuracy
Reduced regulatory risk
Significant operational cost savings
Moreover, ML-driven CoA automation supports audit readiness, as every extracted value can be traced back to its source, maintaining transparency and control.
The variability of Certificate of Analysis formats is a real barrier to automation—but not an insurmountable one. Machine Learning offers a flexible, scalable, and intelligent approach to overcoming this challenge. For any enterprise looking to modernize its quality assurance workflows and stay compliant in a dynamic regulatory environment, ML isn’t just an option—it’s a necessity.