Blogs, News & Articles

The Building Blocks of an Effective IDP Solution: AI, ML, NLP, and More
As businesses struggle to keep up with the explosion of unstructured data, Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) has emerged as a critical tool to automate, extract, and process documents with speed and precision. But what powers this transformative capability? Behind every effective IDP solution lies a powerful combination of technologies: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and more.
Let’s break down these core components and understand how they work together to deliver smart, scalable document automation.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI): The Strategic Brain
AI is the overarching force that orchestrates the entire IDP process. It enables systems to mimic human decision-making by learning patterns and applying logic across different document types.
Role in IDP: AI determines how to classify documents, handle exceptions, and manage workflows based on business rules.
Impact: Reduces manual decision-making, enables autonomous processing, and improves over time with feedback loops.
2. Machine Learning (ML): The Learning Engine
ML empowers IDP systems to get smarter with every document processed. By analyzing historical data and outcomes, the system learns to identify patterns, correct errors, and improve accuracy.
Role in IDP: ML models are trained to recognize invoice layouts, extract relevant fields from contracts, or detect anomalies in financial statements.
Impact: Increases accuracy over time, reduces the need for rule-based coding, and adapts to changing document formats.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP): The Language Translator
NLP allows IDP systems to understand the meaning and context of textual content. This is especially important for semi-structured or unstructured documents like emails, legal agreements, or handwritten notes.
Role in IDP: Enables extraction of key phrases, sentiment, entities (like names, dates, and amounts), and even intent.
Impact: Transforms human language into machine-readable insights, crucial for processing narrative-heavy documents.
4. Computer Vision: The Visual Interpreter
While NLP handles text, Computer Vision tackles images and scanned documents. It allows IDP systems to read content from PDFs, photos, and scanned forms—even those with low image quality or complex layouts.
Role in IDP: Converts images into readable text using Optical Character Recognition (OCR), detects tables, stamps, and signatures.
Impact: Expands IDP applicability to paper-heavy industries like logistics, banking, and healthcare.
5. Optical Character Recognition (OCR): The Text Extractor
OCR is a foundational tool that converts typed, printed, or handwritten text into digital text. While traditional OCR was static, modern OCR integrated with AI and ML boosts accuracy and supports multi-language documents.
Role in IDP: Extracts raw text from scanned files and feeds it into the AI/ML pipeline for further processing.
Impact: Makes legacy documents searchable and usable for automation.
6. Integration and APIs: The Connective Tissue
For IDP to be truly effective, it must seamlessly integrate with existing enterprise systems—ERP, CRM, RPA platforms, and cloud storage.
Role in IDP: Connects data output with downstream systems to automate workflows end-to-end.
Impact: Enables real-time data flow, reduces data silos, and enhances operational efficiency.
The Combined Power: A Real-World Example
Consider a global logistics firm processing thousands of bills of lading and shipping documents daily. With IDP:
OCR + Computer Vision reads scanned documents.
NLP extracts key information like port of loading, consignee name, and commodity details.
ML identifies patterns to flag anomalies or errors.
AI routes documents to the right department or triggers billing in the ERP system.
The result? A 70% reduction in manual data entry and faster turnaround for customs clearance and invoicing.
A modern IDP solution is more than just OCR on steroids. It’s a synergistic system built on AI, ML, NLP, and Computer Vision—working together to transform document chaos into actionable insights. For organizations drowning in paperwork, investing in these building blocks means faster decisions, lower costs, and a significant competitive edge.
As technology continues to evolve, so will the capabilities of IDP—moving from automation to autonomous document processing. The future is not just digital. It’s intelligent.

Why Automating Customer Credit Checks is Key to Risk-Free Growth
For B2B businesses, extending credit is a powerful tool to build customer loyalty and boost sales. But it also comes with risks — delayed payments, bad debts, and cash flow uncertainty. Manual credit checks are no longer fast or reliable enough in today’s high-velocity business environment. That’s why automating customer credit checks is becoming essential to grow securely and smartly.
1. The Challenge of Manual Credit Assessment
Traditionally, assessing a customer's creditworthiness involves pulling financial reports, contacting trade references, setting credit limits based on gut feel, and reviewing aging reports manually. This process is time-consuming, inconsistent, and prone to human error — leading to late interventions and revenue losses.2. Automating Credit Scoring for Smarter Decisions
Modern automation tools can assess credit risk in real-time by integrating multiple data sources — such as credit bureau reports, financial statements, payment histories, and even behavioral insights. AI/ML models evaluate these parameters to assign a dynamic credit score to each customer. This enables consistent, data-driven decision-making without manual intervention.Use Case:
A global distributor implemented AI-powered credit scoring for new customers. The onboarding time dropped by 50%, and the company saw a 30% reduction in bad debt write-offs within a year.3. Setting and Managing Dynamic Credit Limits
With automation, businesses can assign credit limits that evolve with customer behavior. For instance, if a customer consistently pays early, their limit can be automatically increased. If delays are detected, the system can restrict further sales or flag the account for review. This dynamic limit management balances growth with risk control.4. Proactive Alerts for Payment Delays
Automated systems monitor accounts receivable in real-time and generate alerts when payments are overdue or when customers exhibit early signs of financial stress. These alerts help sales and finance teams intervene before issues escalate, enabling faster collections or revised payment terms.Use Case:
A mid-size manufacturer used RPA and alert systems to monitor invoices and customer payment cycles. Early alerts allowed them to renegotiate terms with at-risk accounts and reduce DSO (Days Sales Outstanding) by 12%.5. The Strategic Payoff: Growth Without Guesswork
Automating credit checks isn’t just about protecting receivables. It empowers your sales teams to pursue high-potential accounts confidently, reduces the burden on finance teams, and allows your business to scale without increasing exposure to credit risk. With seamless ERP and CRM integration, credit data becomes part of every decision-making process.
Risk-free growth is possible when finance and sales teams are equipped with intelligent tools. Automating customer credit checks — from scoring and limits to alerts — ensures your business can grow rapidly, responsibly, and resiliently. As economic conditions evolve, automation becomes your frontline defense against uncertainty.
How CoA Automation Sets Contract Manufacturers Apart
As competition intensifies across regulated manufacturing sectors, contract manufacturers are under growing pressure to offer more than just reliable production — they must deliver speed, accuracy, and regulatory-ready documentation. For industries like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, food, and cosmetics, the Certificate of Analysis (CoA) is central to product validation and client trust. Automating the CoA process has become a strategic lever, enabling CMs to streamline operations, enhance compliance, and differentiate themselves in a crowded marketplace.
What is a Certificate of Analysis (CoA)?
A CoA is a critical quality document that verifies a product meets its specified standards. It includes test results, compliance data, batch information, and relevant certifications. For contract manufacturers, CoAs are not just documents — they are proof of performance, quality, and regulatory alignment.
Why CoA Automation Matters Now More Than Ever
With clients expecting faster turnarounds and regulatory bodies tightening scrutiny, manual CoA generation is becoming a liability. Errors, delays, and inconsistent formats can raise red flags during audits, damage client relationships, and even lead to regulatory penalties.
That’s where automation steps in.
By digitizing and automating the CoA creation and distribution process, contract manufacturers can:
Reduce human error
Accelerate product release cycles
Ensure consistency across batches and product lines
Stay audit-ready at all times
Integrate seamlessly with clients’ LIMS, QMS, or ERP systems
The Competitive Advantage of CoA Automation
1. Faster Time-to-Market
Automated CoA systems pull test data directly from laboratory instruments or LIMS, enabling CoA generation in minutes rather than hours or days. For clients working on tight production or distribution timelines, this speed is invaluable.
2. Enhanced Accuracy and Compliance
CoA automation ensures that data is pulled accurately and formatted in a standardized, compliant structure. This minimizes the risk of discrepancies during regulatory audits and builds client confidence.
3. Real-Time Document Delivery
With integrated systems, CoAs can be shared in real time with clients, regulators, or partners. This transparency strengthens collaboration and improves customer satisfaction.
4. Scalable for High-Volume Production
As contract manufacturers take on more clients and SKUs, managing CoAs manually becomes unfeasible. Automated solutions scale effortlessly, ensuring smooth operations even during demand surges.
5. Customization and Branding
Modern CoA automation platforms allow branding and formatting customization based on client needs — a subtle but powerful way to show professionalism and service orientation.
Real-World Impact: A Quick Example
Consider a contract manufacturer serving multiple pharma clients. Previously, each CoA was manually created, reviewed, and emailed, leading to delays and version control issues. After implementing CoA automation integrated with their LIMS and ERP systems:
Turnaround time dropped by 70%
CoA error rates reduced by 95%
Customer satisfaction scores improved significantly due to consistent and on-time documentation
Automating for a Competitive Edge
In a crowded contract manufacturing landscape, CoA automation is more than a back-office improvement — it’s a front-line differentiator. Clients notice when documentation is accurate, timely, and professionally presented. More importantly, regulatory agencies do too.
For forward-thinking contract manufacturers, investing in CoA automation is an investment in operational excellence, customer trust, and long-term growth.

Reducing Fraud in KYC Processes: The Role of Automated Verification
Know Your Customer (KYC) processes are fundamental to maintaining the integrity of financial institutions, fintechs, insurance firms, and even sectors like real estate and telecom. Yet, manual verification methods remain vulnerable to fraud—fake identities, forged documents, and synthetic identity fraud continue to bypass traditional compliance systems. With increasing regulatory scrutiny and rising cases of financial crimes, organizations must find smarter, faster, and more accurate ways to detect and deter fraud. This is where automated KYC verification steps in.
The Growing Threat of Fraud in KYC
Fraud in KYC manifests in many ways—submission of fake IDs, photoshopped documents, use of deepfake technologies for facial recognition, or even stolen identities masked under real-looking paperwork. According to a recent report by the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE), identity fraud cost businesses over $52 billion globally in 2023 alone. A significant portion of these fraud attempts exploited weaknesses in manual onboarding processes.
In a manual setup, document reviewers may overlook subtle signs of tampering or inconsistencies, especially when handling high volumes of applications. Human fatigue, subjective judgment, and lack of real-time cross-validation make it easy for fraudulent profiles to slip through.
Why Automation Is a Game Changer
Automated KYC verification solutions—such as those offered by Star Software—are designed to close the gaps left by manual review. Here’s how:
1. AI-Powered Document Analysis
Advanced AI algorithms can detect anomalies in identity documents, such as mismatched fonts, distorted holograms, or inconsistencies in data fields. These systems compare documents against global databases and use pattern recognition to flag suspicious entries.
2. Real-Time Cross-Validation
Automated tools can cross-reference applicant details with third-party databases (e.g., government registries, sanctions lists, credit bureaus) in real time. This drastically reduces the chances of fraudulent users slipping through undetected.
3. Biometric Verification
Facial recognition and liveness detection technologies ensure that the person submitting the document is physically present and matches the photo on the ID. AI tools are also increasingly capable of detecting deepfakes and manipulated images.
4. Audit Trails and Reporting
Automation platforms maintain detailed logs and generate compliance reports that can be instantly accessed during audits or investigations. This transparency is crucial for regulatory adherence and internal fraud checks.
5. Scalability Without Sacrificing Accuracy
Whether onboarding 50 or 5,000 customers a day, automated systems maintain consistent accuracy. This scalability helps growing companies stay compliant without expanding their KYC teams or compromising fraud detection capabilities.
Real-World Example: Fintech Onboarding
A leading U.S.-based fintech used to take 2–3 days to complete KYC checks manually, with a rejection rate of just 4% for fraudulent documents. After integrating an automated KYC solution powered by Star Software’s platform, their turnaround time dropped to under 5 minutes, and their fraud detection rate improved by 60%, flagging even high-quality fake documents that human reviewers had missed.
As fraudsters become more sophisticated, organizations cannot afford to rely solely on manual KYC processes. Automated verification, driven by AI, OCR, and biometrics, provides a multi-layered shield against fraud. Beyond compliance, it helps build trust with customers, accelerates onboarding, and reduces operational risks.

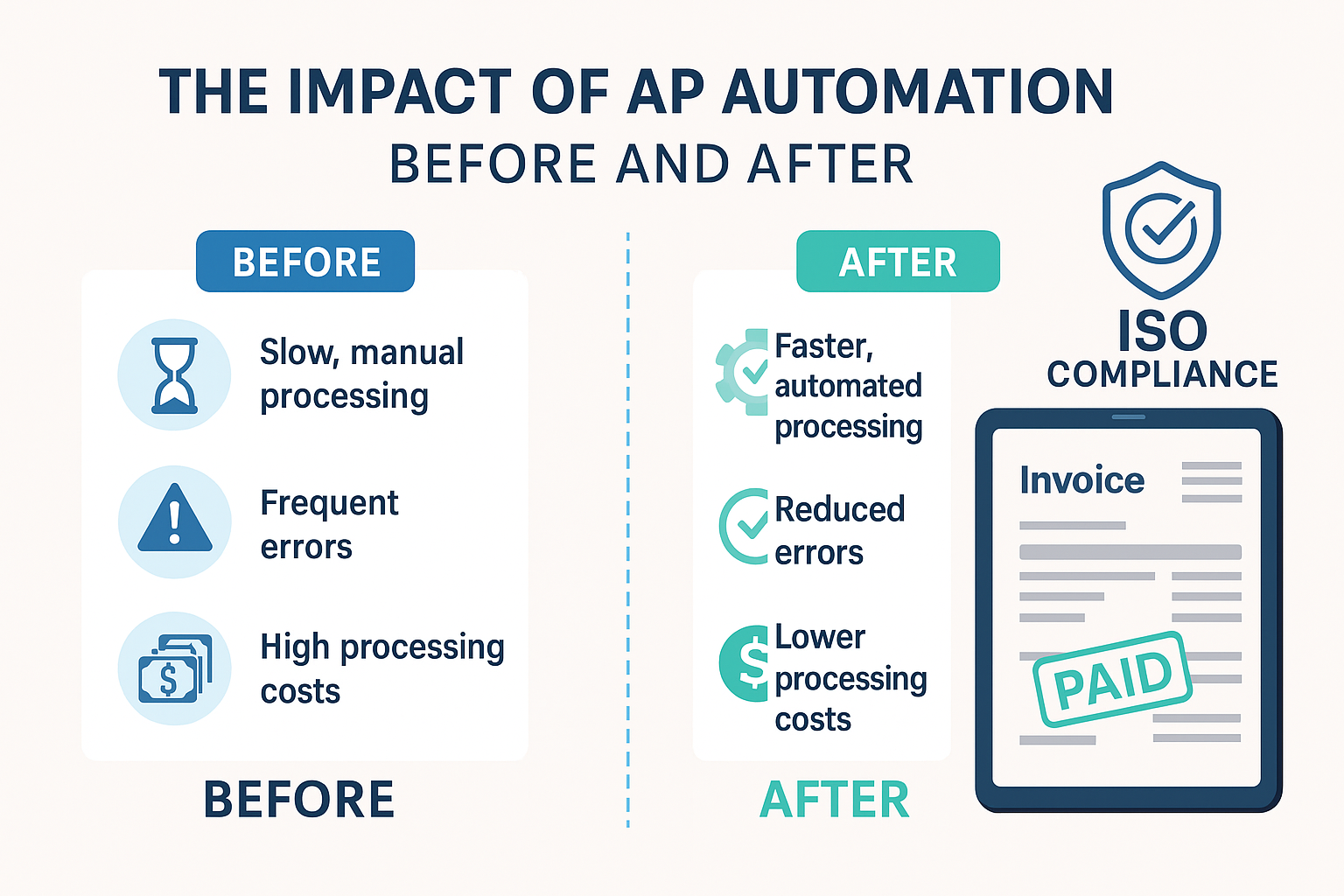
Can Accounts Payable Help You Pass an ISO Audit? Here’s How
When organizations gear up for an ISO 9001 audit, the focus often gravitates toward production, quality control, and documentation processes. But there’s a lesser-known contributor that can tip the scales in your favor—Accounts Payable (AP). Surprisingly, modern AP automation tools not only enhance financial efficiency but also play a crucial role in strengthening ISO 9001 compliance.
Here’s how AP processes, especially when automated, can support your organization’s journey toward passing that all-important audit.
1. Documented Information Control (Clause 7.5)
ISO 9001 requires organizations to maintain documented information in a manner that ensures accuracy, retrievability, and protection against loss. Traditional AP processes involving paper invoices or scattered email approvals make this a challenge.
With AP automation:
Every invoice, approval, and payment record is stored in a centralized digital repository.
Version control and access logs are maintained automatically.
Auditors can trace transactions with a few clicks—ensuring compliance with documentation requirements.
2. Process Consistency and Control (Clause 8.5)
Quality standards thrive on repeatable, standardized processes. Manual AP workflows often involve inconsistencies in approvals, exceptions, and vendor communications.
Automation enables:
Rule-based workflows for approvals and thresholds.
Consistent validation of vendor details and payment terms.
Error reduction through real-time flagging of duplicates or mismatches.
The result? A transparent, controlled process that aligns with ISO’s emphasis on uniformity and predictability.
3. Risk-Based Thinking and Fraud Prevention (Clause 6.1)
ISO 9001 mandates that companies identify and mitigate risks that could impact quality. One such risk lies in unchecked financial transactions—leading to fraud, missed payments, or compliance violations.
An automated AP system offers:
Role-based access controls and audit trails.
Automatic checks for duplicate invoices or supplier anomalies.
Built-in compliance rules to flag exceptions before they escalate.
These features not only reduce financial exposure but also show auditors your proactive stance on risk management.
4. Supplier Relationship Management (Clause 8.4)
Strong vendor performance and reliable supply chains are essential to quality assurance. Delayed or inconsistent payments can harm supplier trust and service levels.
How AP automation helps:
Ensures timely payments through scheduled workflows.
Provides real-time communication on payment status.
Improves vendor satisfaction, which in turn boosts service quality—directly supporting ISO’s objectives.
5. Continuous Improvement (Clause 10.3)
ISO 9001 emphasizes the importance of using data to drive ongoing improvement. Manual AP systems often lack visibility into metrics such as invoice cycle time, error rates, or cost per invoice.
With automation, you gain:
Dashboards and analytics for identifying bottlenecks.
KPIs to benchmark AP performance over time.
Insights that feed into broader process improvement initiatives.
Your AP team becomes more than just a cost center—it becomes a partner in quality and compliance.
The Hidden Hero of Quality Compliance
While Accounts Payable may not be the first department considered in a quality management audit, its automation and alignment with ISO 9001 principles can be a significant advantage. From documentation control to supplier relationships and risk mitigation, an automated AP process helps you meet the expectations of auditors—and run a more efficient operation.
So next time you prepare for an ISO audit, don’t overlook your finance function. A smart, streamlined AP system could be the hidden asset that helps you ace it.